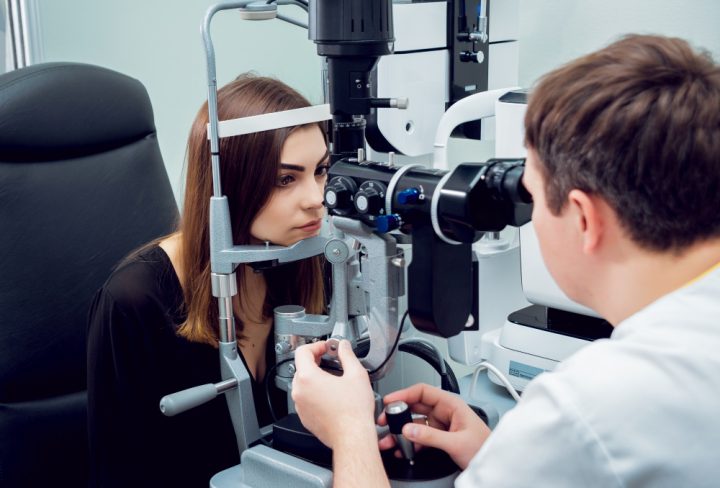
What is Retinal Detachment?
Retinal detachment is a serious eye problem. It happens when the retina, a thin layer at the back of your eye, pulls away from its normal place. Because the retina helps you see, this condition can lead to vision loss if not treated quickly. Early care is important for eye health and vision loss prevention. According to the World Health Organization, retinal detachment is a leading cause of vision problems worldwide.
Common Symptoms of Retinal Detachment
Recognizing retinal detachment symptoms early can help save your sight. Watch for these signs:
However, not everyone will have all these symptoms. If you notice any sudden changes in your vision, act quickly and see an eye specialist.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several things can cause retinal detachment. Some people are at higher risk than others. Here are some common causes and risk factors:
Because some risk factors cannot be changed, regular eye check-ups are important for everyone.
How Retinal Detachment is Diagnosed
Doctors use special tools to check for retinal detachment. First, your eye specialist will ask about your symptoms. Then, they will examine your eyes using bright lights and lenses. Sometimes, they may use ultrasound if the view is blocked. Early diagnosis is key for better outcomes. According to the CDC, prompt treatment can help prevent permanent vision loss.
Surgical Treatment Options
Retinal detachment surgery is often needed to fix the problem. There are several ways doctors can repair the retina:
Your doctor will choose the best surgery based on your eye health and the type of detachment. Most surgeries are done quickly to prevent vision loss.
Recovery and Aftercare
After retinal detachment surgery, proper care is important for healing. Here are some tips for recovery:
Because recovery times can vary, always ask your doctor about what to expect. Most people notice vision improvement over several weeks.
Prevention Tips and Lifestyle Guidance
While not all cases can be prevented, you can lower your risk of retinal detachment with these steps:
Additionally, keeping your eyes healthy helps with vision loss prevention. Simple habits, like wearing sunglasses and eating a balanced diet, also support eye health.
When to See an Eye Specialist
If you notice sudden flashes, floaters, or a shadow in your vision, seek help right away. Early treatment gives you the best chance to save your sight. Even if you are unsure, it is better to be safe and get checked by an eye specialist.
If you notice any sudden changes in your vision, consult an eye specialist promptly for personalized care.